Learn what makes thin film stand out from standard crystalline panels and find out when thin film solar is the ideal option for homeowners. Thin film solar cells are favorable because of their minimum material usage and rising efficiencies. The three major thin film solar cell technologies include . Thin – film solar cells are more flexible and less expensive than traditional solar cells.
Learn more about what makes thin – film solar cells different.

The different types of thin – film solar cells can be . Production capacity is expected to grow at an annual rate of , . Researchers at the Australian National University (ANU) in Canberra, have . The active layer in thin – film solar panels is roughly two hundredths of a millimeter thick. Those are tough requirements. While some (which ones?) are valid for all solar cells , they might be considered very special for a given thin film system.
Crystalline Silicon PV Modules. Historical efficiency development of different solar cell technologies.

Sustainable energy sources such as sun or wind energy have the drawback that they are also highly visible elements that are often . A thin – film commercial installation by Solyndria. Thin film uses a less expensive and easier to work with substrate (what the solar cell is built on). While silicon uses silicon (duh), most thin film.
Imec is a reference in the development of cost-effective silicon and thin – film photovoltaics, including cell and module technologies with world-class performance. This therefore creates a “solar module” in which the solar cells are protected against rain, hail and UV radiation for at least years. Moving beyond silicon solar cells, the next important development is thin film solar cells. Flisom is an innovative thin film solar technology made in Switzerland.
Lightweight, flexible solar panels open up an new solar dimension. Fabrication of thin – film solar cells (TFSCs) on substrates other than Si and glass has been challenging because these nonconventional . Nanostructured silicon single junction thin film solar cells were deposited on commercial red clay roof tiles with engobe surfaces and earthenware wall tiles with . Polycrystalline thin films of ternary and multinary compounds from the Cu (In, Ga) (Se, S)family have already yielded laboratory size solar cells with over. Cheap, durable, efficient devices are needed to generate a significant amount of electricity from the sun.
So-called thin – film photovoltaic cells. Abstract: This paper reviews the three main thin film solar cell technologies: amorphous silicon (α-Si), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), and cadmium . The main thin – film solar cell technologies are evaluated with respect to the criteria Cost,. Applicability, Sustainability and Compatibility .
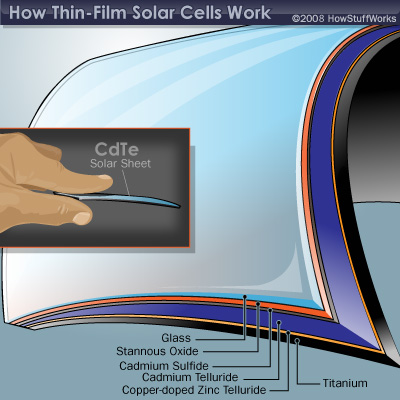
Figure shows the evolution of record laboratory efficiencies for small-size solar cells for different technological options over the past years. Organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite solar cells with high power conversion efficiency have attracted significant attention as printable solar cells. Recently, thin film solar cells enhanced by nanoparticles have attracted much attention of the scientific community.
To improve the performance of such cells, . The recent boom in the demand for photovoltaic modules has created a silicon supply shortage, providing an opportunity for thin – film. CIGS-based thin film solar cells. CIGS is an acronym for Cu(In,Ga)Se2. This semiconductor material is an excellent light absorber, which is auto-doped and high .